Sunprotection - Skin Cancer Clinic
The sun gives us vitamin D, but too much sun and the use of solariums are the most important causes of skin cancer in Norway. Around 9 out of 10 cases are due to UV radiation.
At the Skin Cancer Clinic you will meet experienced dermatologists who can examine skin changes, give you advice on sun protection and offer treatment.
- No referral required

This is why the sun and solariums increase the risk of skin cancer
Sunlight contains ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is mainly made up of UVA and UVB rays. While UVB rays are the primary cause of sunburn, UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and contribute to skin aging and wrinkles.
Both types of UV radiation can damage the DNA (hereditary material) of skin cells. Although the body has mechanisms to repair such damage, repeated and prolonged exposure can overwhelm these systems. Over time, this DNA damage can cause cells to start growing out of control, which can lead to skin cancer.

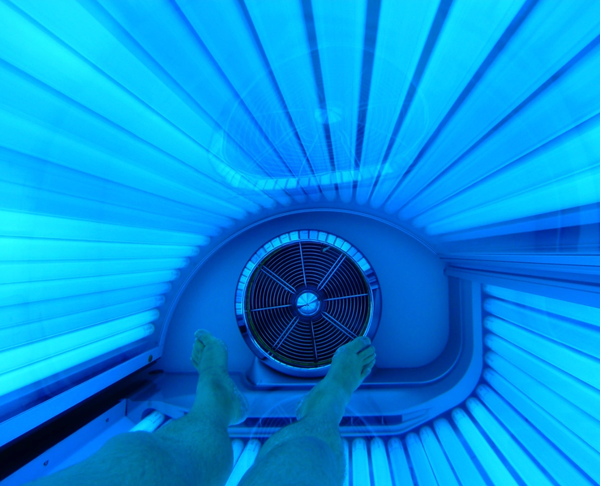
Solarium - a documented risk
Solariums expose the skin to concentrated and intense UV radiation, often many times stronger than the summer sun at midday. This radiation significantly increases the risk of all types of skin cancer, including mole cancer.
The risk is particularly high if you start using a solarium at a young age; studies show a significantly increased risk when using before the age of 35. There is no safe lower limit for solarium use.
At Hudkreftklinikken, our dermatologists strongly advise against all use of solariums, as it is a documented cause of skin cancer.

Who is most at risk?
Although all skin types can develop skin cancer from excessive UV exposure, some groups are more vulnerable than others. You are at higher risk if you:
- Have fair skin (skin type 1 or 2) that sunburns easily and rarely or never tans.
- Have many moles (over 50-100), or large and irregular moles.
- Have been sunburned repeatedly, especially in childhood and adolescence.
- Have a close family history of skin cancer (genetic predisposition).
- Are taking medications that weaken the immune system (immunosuppressive therapy).
- Have had skin cancer in the past.
- Have spent a lot of time outdoors over many years without adequate protection.
Knowing your own risk profile can help you take better precautions and be more aware of the importance of regular skin and mole checks.

Skin cancer in Norway
Did you know that Norway unfortunately ranks among the world's top countries for the incidence of melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer? The number of cases of both melanoma and other skin cancers has been increasing for decades.
The primary reason for this is our sun habits, including excessive sunbathing and use of solariums. In fact, around 9 out of 10 cases of skin cancer in Norway are related to too much UV radiation from the sun or solariums.
Fortunately, the prognosis is good if skin cancer is detected and treated early. Therefore, it is important to know the risk factors and be aware of skin changes.
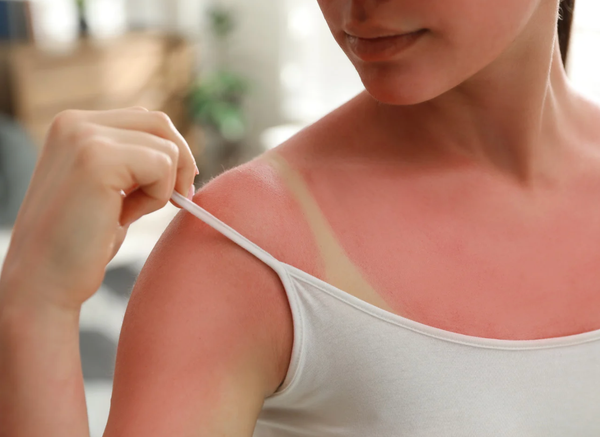

Protection
Limit time in strong sun: The sun is usually strongest between 12 PM and 3 PM. Try to reduce your time in direct sunlight during this period.
Seek shade: Taking breaks in the shade gives your skin a rest from the most intense radiation. Use parasols, trees, or other shaded areas.
Wear protective clothing: Light, covering clothing, a wide-brimmed hat that shades your face, ears, and neck, and CE-marked sunglasses provide good physical protection.
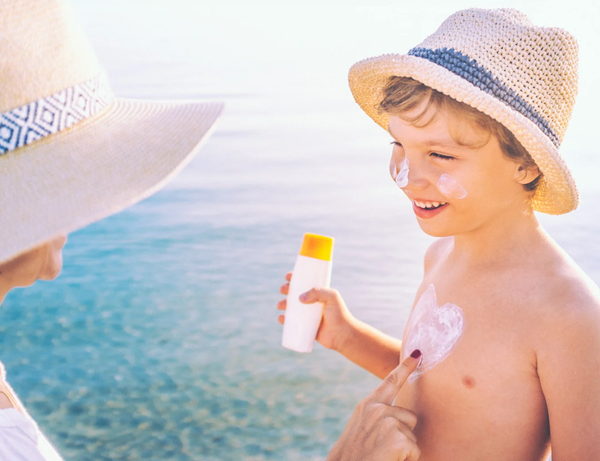
Use sunscreen correctly: Choose a sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and UVA/UVB protection. Apply generously (a handful for the whole body) 15-30 minutes before going out. Reapply every two hours, and more often if you swim, sweat a lot, or towel dry. Don't forget exposed areas like ears, lips, neck, and feet.
Avoid tanning beds: Tanning beds expose your skin to strong UV radiation and significantly increase the risk of skin cancer. There is no safe way to use a tanning bed.

Mole check
A mole check is a quick and thorough examination of your moles. Our dermatologists look for warning signs such as asymmetry, irregular edges, changes in color or size, itching or bleeding. During the consultation, the doctor will examine your mole(s) carefully, including with a dermatoscope (a magnifying glass with a light) to assess whether everything looks normal. After the examination, you will receive a clear assessment: either a message that the mole is harmless, or a recommendation for follow-up or removal if something should be treated.
👉 Tip: Most changes in moles are not dangerous, but early detection of skin cancer (mole cancer) is important. Please read our article on mole cancer (melanoma) for more information about which signs you should pay attention to.
Book appointment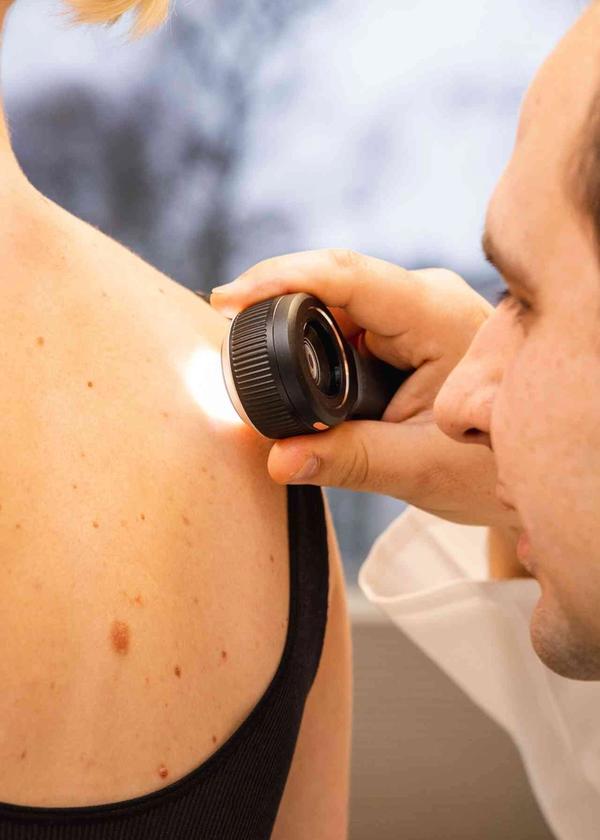
If a mole is suspicious, bothersome or cosmetically disturbing, we offer safe mole removal at Dr.Dropin. Our experienced doctors first assess whether the mole should be removed – often this can be done in the same consultation if you wish. The removal itself is performed under local anesthesia, so it is practically painless. The doctor gently removes the mole with a small margin around it, to ensure that all abnormal tissue is removed. For your safety, the mole that is removed is usually sent for analysis in a laboratory, so that we can rule out any skin cancer changes. You will receive an answer within approximately 1–2 weeks. Afterwards, the wound will heal within a few weeks, and we will advise on care for the best possible healing with the least possible scarring.
Our general practitioners can remove most common moles, while dermatologists take care of larger or more complicated cases. In any case, you can expect safe treatment from us.
Book appointment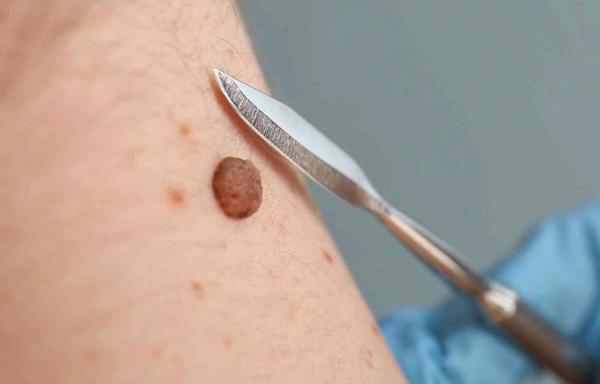
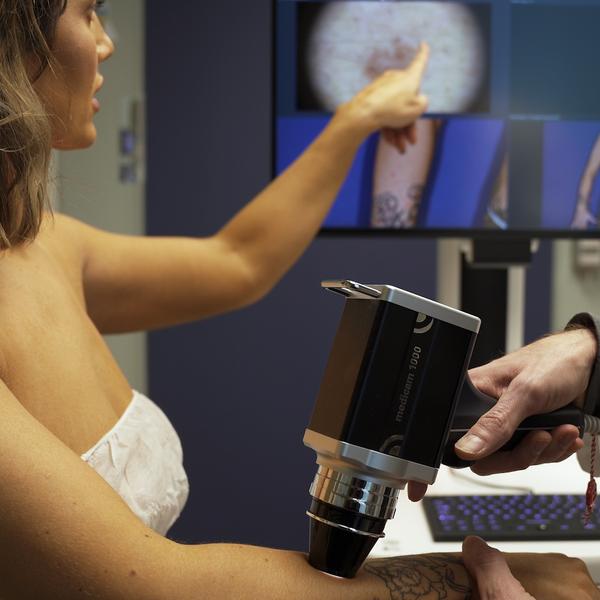
For those of you who want an extra thorough check of all your moles, we offer FotoFinder mole screening – the most advanced mole check on the market. FotoFinder is a digital camera and computer system that photographs your entire body and creates a detailed map of your skin and moles. This advanced technology makes it possible to detect small changes over time by comparing images from each check. Suspicious moles are magnified and carefully assessed by the dermatologist using high-resolution images (videodermatoscopy), which increases the accuracy of the assessment.
Book appointment